 Zrzyzeni Zemske knizeczstwi tiessynskeho, 1573 Zrzyzeni Zemske knizeczstwi tiessynskeho, 1573
The property statute of the Duchy of Cieszyn, written in 1573, on the order of Prince Wenceslas III, was intended to regulate the legal relationship between the prince and the local nobility. Held in question for many years by the Cieszyn people, it was only finally confirmed in 1591. It remained the fundamental legal statute for the regulation of the lives of the people of the Duchy of Cieszyn until the mid-19th century. |
 Register of Cieszyn’s Ducal Chancellery, 1549-1609 Register of Cieszyn’s Ducal Chancellery, 1549-1609
The book containing entries of documents issued in the Chancellery of Cieszyn’s dukes: Wenceslaus, Katarzyna Sydonia and Adam Wenceslaus.
|
 Registra a Knihý Zemske, 1591-1601 Registra a Knihý Zemske, 1591-1601
The book with awards of Cieszyn County Court with competency over all issues related to the gentry. The County Court of Cieszyn was established in the 15th century, originally it adjudicated in disputes based on Moravian and Polish common laws, later it relied on the county law of Cieszyn written down in 1573.
|
 Regystra Hlawny Zamku Tiessynskeho, 1577 Regystra Hlawny Zamku Tiessynskeho, 1577
Cieszyn’s land census record (urbarium) of 1577 containing the list of tax liabilities paid by the inhabitants of the following villages and towns: Cieszyn, Zamarski, Gumna, Ogrodzona, Kisielów, Godziszów, Goleszów, Cisownica, Cisownica Mała, Kozakowice, Bażanowice, Żuków Dolny, Trzycież, Mistrzowice, Mosty, Sibica, Ligotka Kameralna, Krasna, Mnisztwo, Gułdowy, Puńców, Oldrzychowice, Tyra, Guty, Marklowice Górne, Bystrzyca, Gródek, Nawsie, Milików, Jabłonków, Piosek, Bukowiec, Mosty near Jablunkov. |
 Wenceslaus, the Duke of Cieszyn and Great Głogów, issues regulations for the butchers’ guild of Cieszyn, 1574 Wenceslaus, the Duke of Cieszyn and Great Głogów, issues regulations for the butchers’ guild of Cieszyn, 1574
Parchment document, issued in Cieszyn on Wednesday before St. Catherina’s Day in 1574. Ducal seal on a parchment strip.
|
 Adam Wenceslaus, the Duke of Cieszyn and Great Głogów, confirms guild privileges for butchers of Cieszyn, 1574 Adam Wenceslaus, the Duke of Cieszyn and Great Głogów, confirms guild privileges for butchers of Cieszyn, 1574
Earlier privileges for the winemakers guild had been issued in 1583 and 1587. Parchment document, issued in Cieszyn on Wednesday after St. Michael’s Day in 1598. Ducal seal on a yellow and blue cord.
|
 Elizabeth Lucretia, Duchess of Cieszyn, confirms all earlier privileges and rights granted to the knight and gentry class of the Duchy of Cieszyn by her ancestors, 1625 Elizabeth Lucretia, Duchess of Cieszyn, confirms all earlier privileges and rights granted to the knight and gentry class of the Duchy of Cieszyn by her ancestors, 1625
Parchment document, issued in Cieszyn on Thursday before St. Matthew’s Day, 1625. Ducal seal on a parchment strip.
pasku. |
 Elizabeth Lucretia, Duchess of Cieszyn, confirms all earlier privileges granted to the mayor, council and inhabitants of Cieszyn by Dukes, 1626 Elizabeth Lucretia, Duchess of Cieszyn, confirms all earlier privileges granted to the mayor, council and inhabitants of Cieszyn by Dukes, 1626
Parchment paper, issued in Cieszyn on Wednesday, on the Day of Sending the Apostles, 1626. Ducal seal on a parchment strip.
|
 Empress Maria Teresa grants the baron title and coat of arms to Rudolf Celestyn from Celestyn, Vienna, 16 June 1767 Empress Maria Teresa grants the baron title and coat of arms to Rudolf Celestyn from Celestyn, Vienna, 16 June 1767
The book with red velvet binding, parchment sheets. Empress seal in a metal box on golden cord.
|
 Joseph II, emperor, confirms all privileges granted to the Town of Strumień in 1482-1670, Vienna, 4 September 1783 Joseph II, emperor, confirms all privileges granted to the Town of Strumień in 1482-1670, Vienna, 4 September 1783
The book contains copies of municipal privileges from 1482-1670. Parchment book, emperor seal fixed to a yellow cord.
|
 Municipal book of Cieszyn, 1556-1629 Municipal book of Cieszyn, 1556-1629
It contains testaments of Cieszyn’s burghers, including the will of Jadwiga Trzanowska, mother of Priest Jerzy Trzanowski, author of the book of religious songs Cithara Sanctorum from 1620.
|
 Municipal book of Cieszyn, 1577-1594 Municipal book of Cieszyn, 1577-1594
It contains records of sales contracts made by Cieszyn’s burghers. Book binding with blinds and white leather.
|
 Einnehmen Brughaller, 1519 Einnehmen Brughaller, 1519
Accounting book of the city of Cieszyn. The book binding with raw lime planks and sewn sections.
|
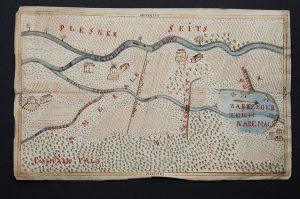 The map of boundary between the Duchy of Cieszyn and Pszczyna and Bielsko counties, 18th century. The map of boundary between the Duchy of Cieszyn and Pszczyna and Bielsko counties, 18th century.
The border in the area of Zabrzeg. |
 Design of the Theater of Cieszyn, [1908] Design of the Theater of Cieszyn, [1908]
The theater was built in 1910, based on the design by a well-known Vienna company Fellner-Helmer.
|
 The view on Cieszyn, 1876 The view on Cieszyn, 1876
The photograph of the Głęboka Street and the castle hill with the Hunters Palace.
|
 Assignats, 1919 Assignats, 1919
Substitute paper money used in Cieszyn under the ruling of the National Council of Duchy of Cieszyn, the first Polish governmental body in the reestablished Polish country.
|
















